May 2019
Archer Western completes Biocontainment Critical Care Unit at UTMB Galveston
GALVESTON, TEXAS – The fight against infectious diseases received a significant boost with Archer Western's completion of the biocontainment critical care unit at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston (UTMB). The $17 million project is one of 10 regional centers in the United States specially designed to treat patients exposed to highly infectious diseases, such as Ebola. The biocontainment units are biosafety level-4 (BSL-4) laboratories, highly secure medical units that serve patients diagnosed or suspected of having a disease that poses extraordinary risk to the population and prevents accidental infection of workers or release into the surrounding community.
The space was designed by Shah Smith & Associates with appropriate technology and facility systems capable of total isolation and adhered to protocols required in BSL-4 laboratories. Archer Western’s work included the renovation of the hospital's existing emergency department into a facility that can accommodate events involving extremely infectious and deadly diseases.
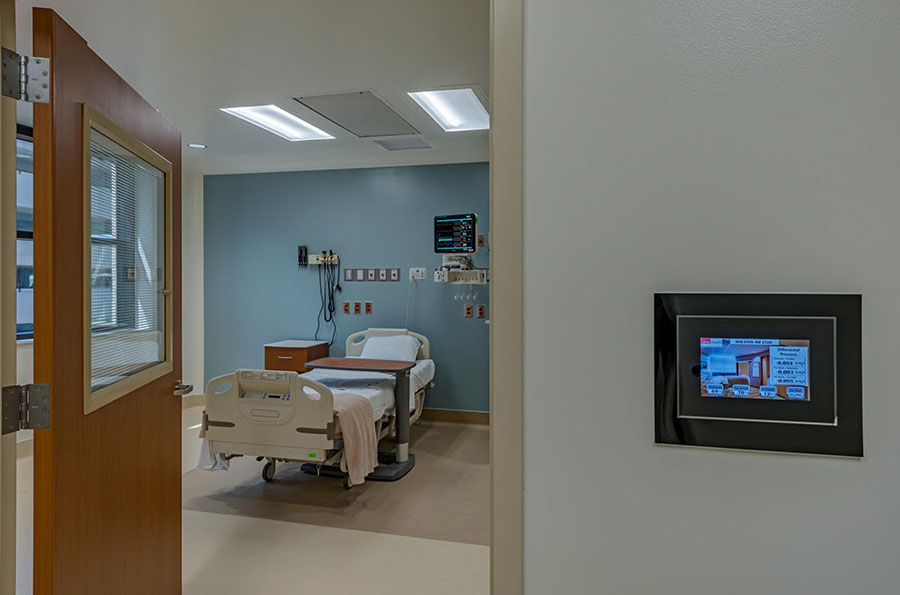
UTMB's biocontainment critical care unit is able to admit and treat up to six patients, including those diseases designated for quarantine by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). The design includes tools necessary for handling these extremely sensitive medical cases, including emergency decontamination showers, intercom systems and a biosafety hood where staff can prepare samples in a contained space.
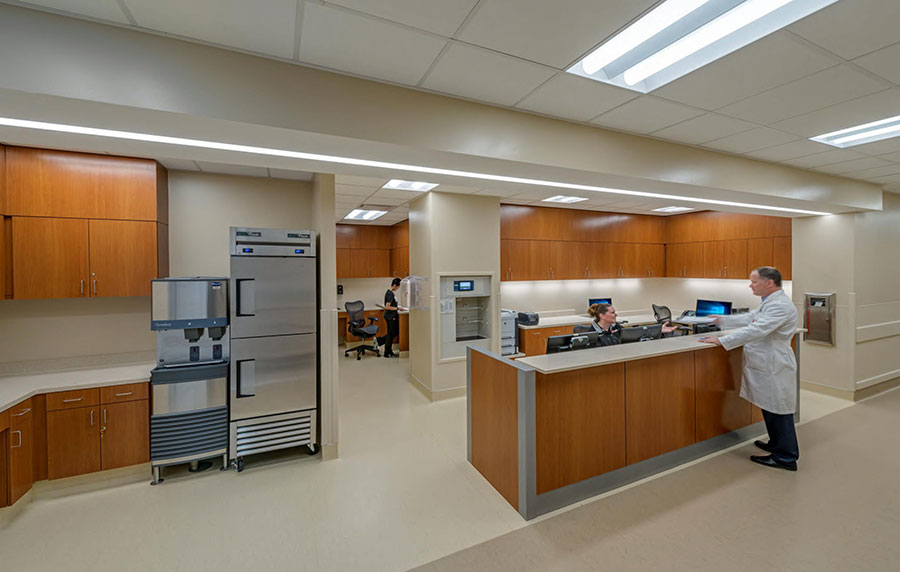

Each patient suite contains bathrooms with toilets and showers. Each room also has a window and intercom connecting it to an area where healthcare workers can communicate with the patient without putting on protective equipment. The design dedicates a substantial amount of space to staff work areas as well. Adjacent to the main treatment room is an anteroom with a hands-free sink as well as a staff prep room with lockers and a shower for emergency decontamination. The work space includes its own biosafety hood, where staff can prepare samples in a contained space and an adjacent dedicated lab that can be used to test for pathogens, do blood tests and other essential procedures.
Negative air pressure, continuously tracked by multiple digital pressure monitors, keeps clean air flowing in from the hallways into the anteroom, from the anteroom into the patient rooms, and then exhausted out through high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters being released more than seven feet above the hospital's roofline. Each room has full air exchange on average every five minutes.
UTMB is the disease-fighting command center of Texas. Across the 84-acre campus, there are three different disease-fighting facilities, two of which are the training center and the new special biocontainment hospital wing designed to treat patients who've come in contact with fast-spreading, high-mortality pathogens. At the heart of the campus is the eight-story Galveston National Laboratory (GNL), which studies and tracks emerging infectious diseases and defends against bioterrorism. The new biocontainment unit at UTMB will primarily serve Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma and New Mexico.
Click here to read more about the biocontainment critical care unit.